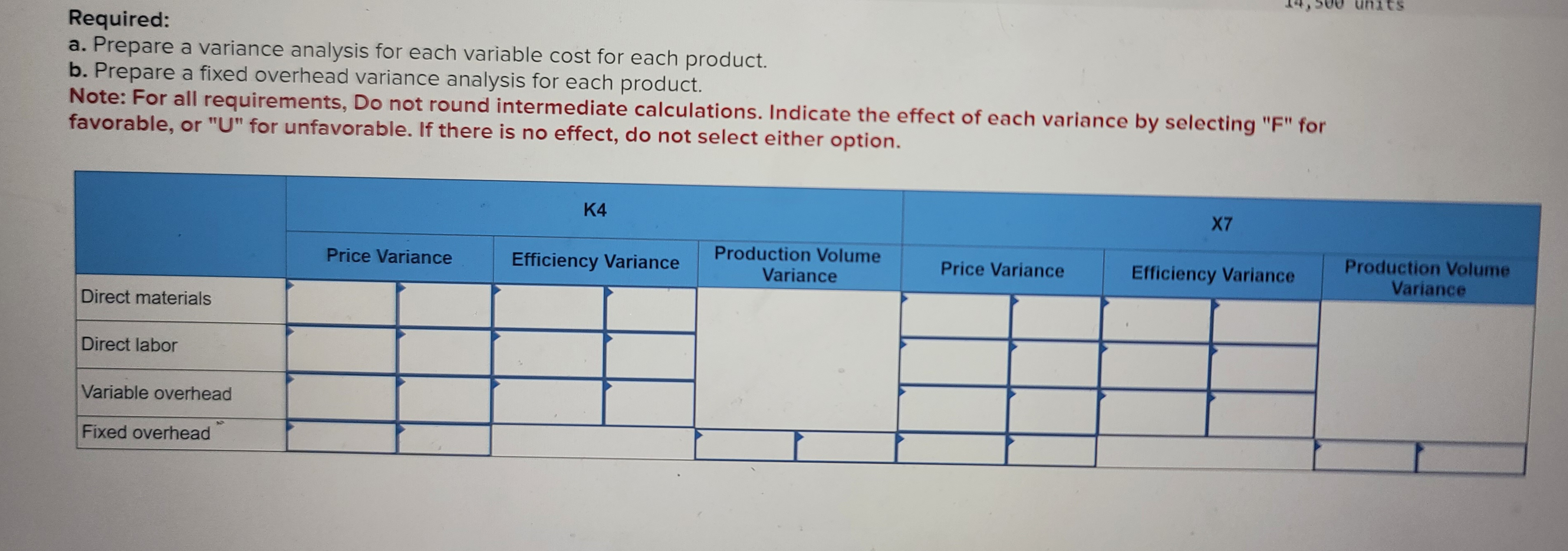
If the total actual cost is higher than the total standard cost, the variance is unfavorable since the company paid more than what it expected to pay. Unfavorable efficiency variance means that the actual labor hours are higher than expected for a certain amount of a unit’s production. It is crucial as it flags discrepancies between planned and actual labor indirect tax services hours, pinpointing inefficiencies. This data prompts a focused investigation into production bottlenecks, enabling corrective action. Addressing these discrepancies enhances resource utilization, productivity, and cost control, which is vital for optimizing operations and ensuring the efficient use of labor within a business or manufacturing setting.
Analysis
Calculating and managing direct labor efficiency variance is essential for controlling labor costs in the construction industry. By understanding the formula, knowing the key factors that impact labor efficiency, and implementing best practices like using time-tracking software, you can reduce inefficiencies and improve your project’s profitability. One of the best ways to monitor labor efficiency is, for sure, using time-tracking software. For example, advanced tools like SmartBarrel’s workforce management solutions provide real-time insights into labor usage on the construction site. It gives you accurate data on direct labor hours, so you’ll be able to quickly identify inefficiencies and eradicate them before they impact the project’s budget. In this example, the Hitech company has an unfavorable labor rate variance of $90 because it has paid a higher hourly rate ($7.95) than the standard hourly rate ($7.80).
- Actual labor costs may differ from budgeted costs due to differences in rate and efficiency.
- The actual results show that the packing department worked 2200 hours while 1000 kinds of cotton were packed.
- Note that both approaches—the direct labor efficiency variancecalculation and the alternative calculation—yield the sameresult.
- The more Direct Labor Mix Variance is decreased, the less wasted resources are on production, and the better chance there is that products will be produced within their optimal amount of time.
- Direct Labor Yield Variance (DLYV) is a measure of the difference between actual and expected labor costs, based on the number of units produced or services provided.
- Excessive inventories, particularly those that are still in process, are considered evil as they generally cause additional storage cost, high defect rates and spoil workers’ efficiency.
What are the benefits of calculating direct labor yield variance?
The first option is not in line with just in time (JIT) principle which focuses on minimizing all types of inventories. Excessive inventories, particularly those that are still in process, are considered evil as they generally cause additional storage cost, high defect rates and spoil workers’ efficiency. Due to these reasons, managers need to be cautious in using this variance, particularly when the workers’ team is fixed in short run. In such situations, a better idea may be to dispense with direct labor efficiency variance – at least for the sake of workers’ motivation at factory floor.
Direct Labor Mix Variance FAQs
He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. The management estimate that 2000 hours should be used for packing 1000 kinds of cotton or glass. It is a very important tool for management as it provides the management with a very close look at the efficiency of labor work. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Additionally, the dynamic nature of industries, with evolving technologies and practices, swiftly renders established standards obsolete, demanding frequent revisions.
Causes of direct labor rate variance
Hitech manufacturing company is highly labor intensive and uses standard costing system. Direct labor rate variance is equal to the difference between actual hourly rate and standard hourly rate multiplied by the actual hours worked during the period. The variance would be favorable if the actual direct labor cost is less than the standard direct labor cost allowed for actual hours worked by direct labor workers during the period concerned. Conversely, it would be unfavorable if the actual direct labor cost is more than the standard direct labor cost allowed for actual hours worked.
United Airlines asked abankruptcy court to allow a one-time 4 percent pay cut for pilots,flight attendants, mechanics, flight controllers, and ticketagents. The pay cut was proposed to last as long as the companyremained in bankruptcy and was expected to provide savings ofapproximately $620,000,000. Thedirect labor rate variance would likely be favorable, perhapstotaling close to $620,000,000, depending on how much of thesesavings management anticipated when the budget was firstestablished. From the payroll records of Boulevard Blanks, we find that line workers (production employees) put in 2,325 hours to make 1,620 bodies, and we see that the total cost of direct labor was $46,500. Based on the time standard of 1.5 hours of labor per body, we expected labor hours to be 2,430 (1,620 bodies x 1.5 hours).
In this question, the Bright Company has experienced a favorable labor rate variance of $45 because it has paid a lower hourly rate ($5.40) than the standard hourly rate ($5.50). Favorable variance means that the actual labor hours’ usage is less than the actual labor hour usage for a certain amount of production. Note that both approaches—direct labor rate variance calculationand the alternative calculation—yield the same result. This formula gives you a clear picture of how much the actual labor usage deviated from the budgeted amount. A positive result indicates greater efficiency (i.e., less time was needed), while a negative result highlights inefficiencies (more time was used than planned). This $150 variance indicates that the company exceeded the expected labor hours, resulting in increased production costs.
The flexible budget is comparedto actual costs, and the difference is shown in the form of twovariances. It is defined as the differencebetween the actual number of direct labor hours worked and budgeteddirect labor hours that should have been worked based on thestandards. In other words, when actual number of hours worked differ from the standard number of hours allowed to manufacture a certain number of units, labor efficiency variance occurs.